Moringa (Moringa oleifera) is a nutrient-rich tree native to India but also grown in other tropical and subtropical regions.
Often called the “miracle tree,” nearly all parts of the plant—leaves, pods, seeds, and roots—are used for their medicinal and nutritional properties.
- Nutritional powerhouse: Moringa leaves are rich in vitamins (A, C, E), minerals (calcium, potassium, iron), protein, and antioxidants.
- Health benefits: It is known for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and blood sugar-regulating properties. It supports skin health, boosts energy, and strengthens the immune system.
- Forms: Moringa is consumed as fresh leaves, powder, capsules, or tea.
- Uses: Traditionally used in herbal medicine, moringa is now widely available as a dietary supplement due to its high nutritional content.
Moringa is popular for its potential to address malnutrition and boost overall wellness.
- Nutrient Supplement: Moringa is rich in vitamins (A, C, and E), minerals (calcium, potassium, and iron), and protein. It helps fill nutritional gaps.
- Antioxidant Properties: Moringa contains powerful antioxidants, such as quercetin and chlorogenic acid, which help fight oxidative stress and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Moringa’s compounds, like isothiocyanates, may reduce inflammation, which is linked to various health issues like arthritis and heart disease.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Some studies suggest that moringa may help lower blood sugar levels, making it potentially beneficial for people with diabetes.
- Cholesterol Reduction: Moringa may lower cholesterol levels, which could support heart health.
- Boosts Energy: The nutrients in moringa, such as iron, may help reduce fatigue and improve overall energy levels.
- Supports Skin Health: Due to its high vitamin A and E content, moringa may promote healthy skin by protecting it from damage and enhancing its glow.
- Supports Digestion: Moringa has mild laxative properties and can help support digestion and bowel health.
- Immune Support: The rich nutrient content in moringa may strengthen the immune system, helping the body fight off infections and illnesses.
- Supports Brain Health: The antioxidants in moringa might help protect brain function and improve cognitive performance.
Serving Size: 100 grams (MORINGA powder)
- Calories: 300–375 kcal
- Protein: 25–27 grams
- Carbohydrates: 50–60 grams
- Sugars: ~10 grams
- Fiber: 30–35 grams
- Fat: 5–7 grams
- Saturated fat: ~1.5 grams
- Vitamins:
- Vitamin A (from beta-carotene): 16,000–20,000 IU (~300–350% DV)
- Vitamin C: ~18–20 mg (~20–25% DV)
- Vitamin E: ~80 mg (~500% DV)
- Vitamin K: ~850 mcg (~700% DV)
- B Vitamins (B1, B2, B3): small amounts
- Minerals:
- Calcium: 2,000–2,500 mg (~200% DV)
- Iron: 28–32 mg (~150–175% DV)
- Potassium: 1,300–1,500 mg (~30–35% DV)
- Magnesium: 300–400 mg (~90–100% DV)
- Phosphorus: ~250 mg (~35% DV)
- Zinc: ~2–3 mg (~25% DV)
Key Highlights:
- High in protein: Suitable for plant-based diets, moringa powder offers a significant amount of protein.
- Rich in fiber: Promotes digestive health.
- High in antioxidants and vitamins: Particularly vitamin A and E, beneficial for skin, vision, and immunity.
- Good source of minerals: Moringa provides calcium, iron, and magnesium, which are essential for bone health, red blood cell formation, and muscle function.
| ATTRIBUTES | NON-GMO, NON-IRRADIATED, ORGANIC, VEGAN |
|---|---|
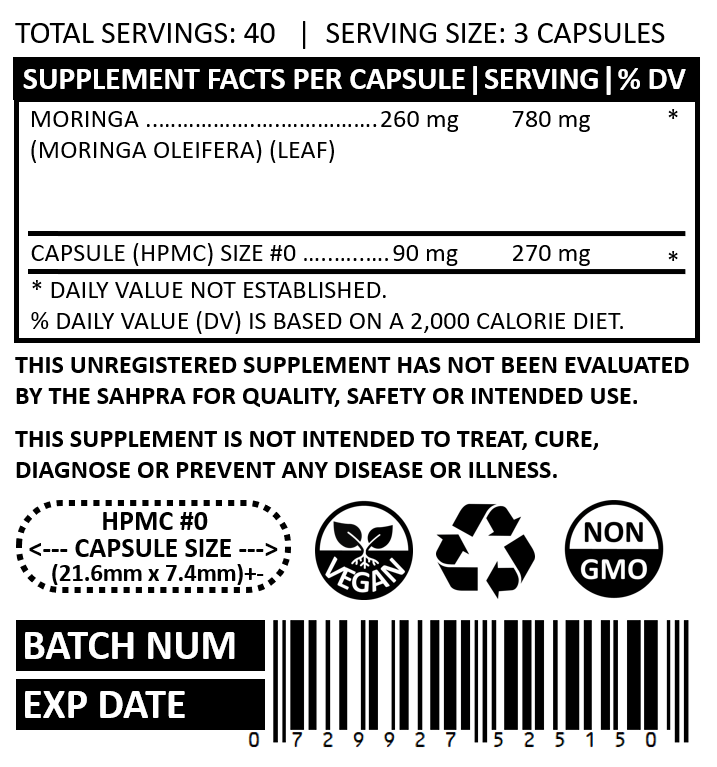
| BARCODE | 0729927525150 |
| CAPSULE COUNT | 120 |
| CAPSULE DIMENSIONS | SIZE #0 | 21.6mm x 7.4mm |
| CAPSULE TYPE | HPMC (VEGAN) |
| CAUTION | Pregnant/nursing mothers, children and individuals with a medical condition should consult a physician before using this dietary supplement. |
| DISCLAIMER | This unregistered supplement has not been evaluated by the SAHPRA for quality, safety or intended use. This supplement is not intended to treat, cure, diagnose or prevent any disease or illness. |
| INCI | MORINGA OLEIFERA |
| INGREDIENTS | MORINGA (260mg) PER CAPSULE (90mg) HPMC |
| REF | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moringa_oleifera |
| SAHPRA | NOT EVALUATED |
| SCHEDULE LEVEL | [S0] SCHEDULE LEVEL ZERO |
| SERVING SIZE | 3 CAPSULES |
| SERVINGS | 40 SERVINGS |
| SKU | VV2410-131518914 |
| SUGGESTED USE | 3 CAPS, ONCE DAILY |
| SUPPLY | 40 DAYS |
| WARRANTY | NON RETURNABLE |